《A Brief History of Intelligence》
outdated myth of 3 layers
- instincts/emotions/cognition
- do not delineate clealy and span all supposed layers
⠀
0 First Neurons: Reflex
multicellular life birthed neurons
- invented digestion VS engulfing single-celled life
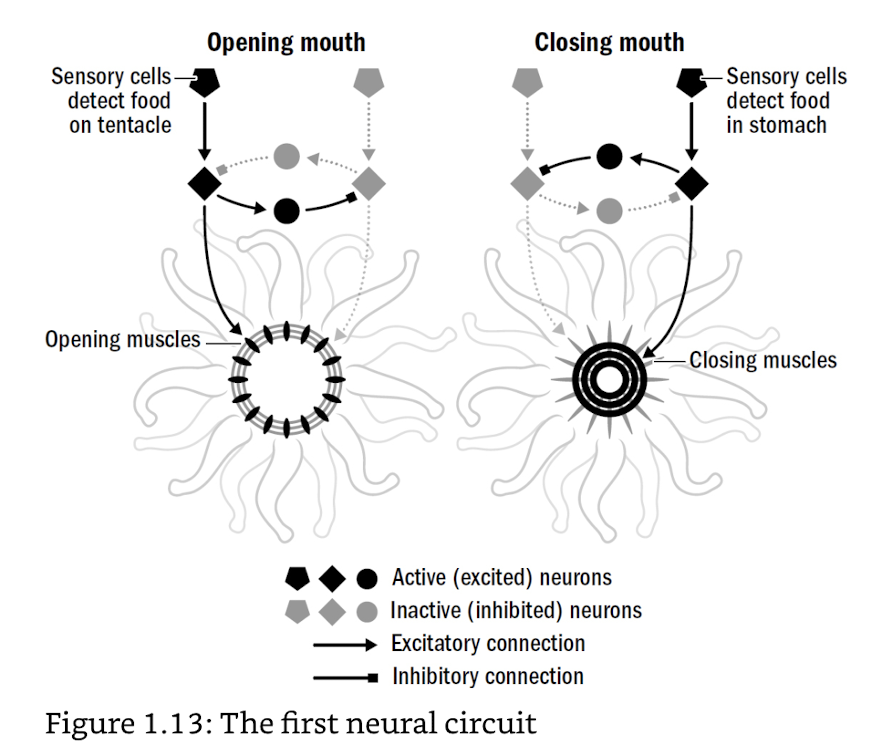
- coral-like reflex to sense & respond to food
⠀
neuron uinversal features
- all-or-nothing spikes: can respond to subtle stimuli
- rate coding: strength-sensitive
- adaptation: adjust threshold to avoid under- or overstimulation
- excitatory/inhibitory synapses: enables logic
⠀
1 Breakthrough: Steering
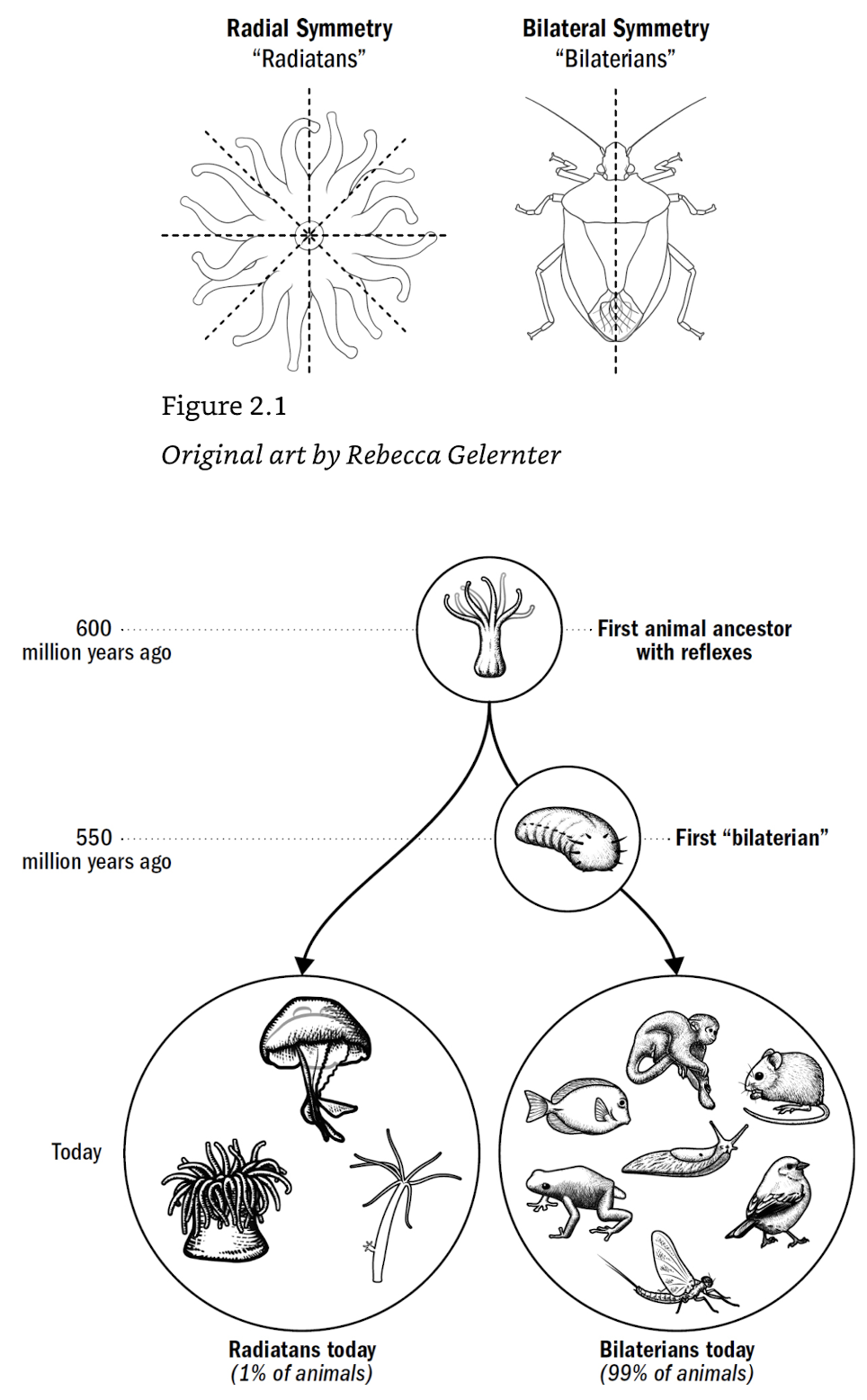
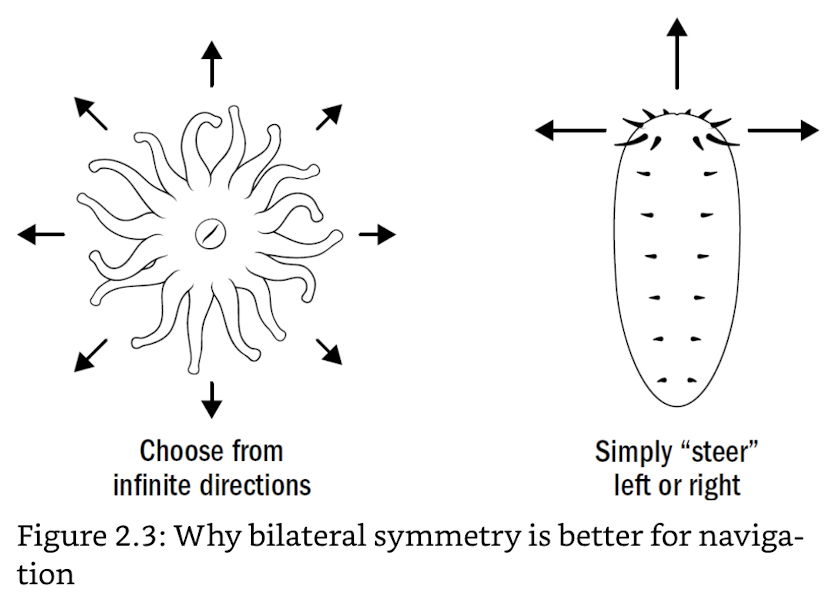
bilaterians birthed brains for steering
- radially symmetrical (wait for food) → bilateral (go to food)
- move forward + turn
- multicellular: stimuli → neurons → muscle (VS single-celled steering requires no neurons)
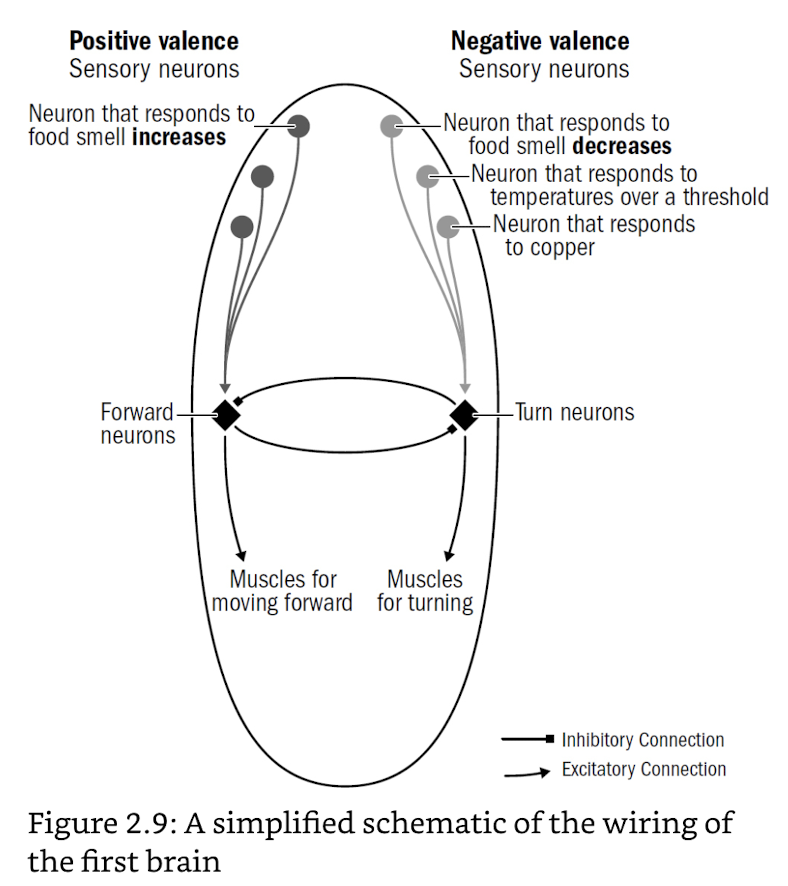
- brain = integration of voting
- diff sensory cells vote for steering in diff directions
- calculates trade-offs & makes single decision
⠀
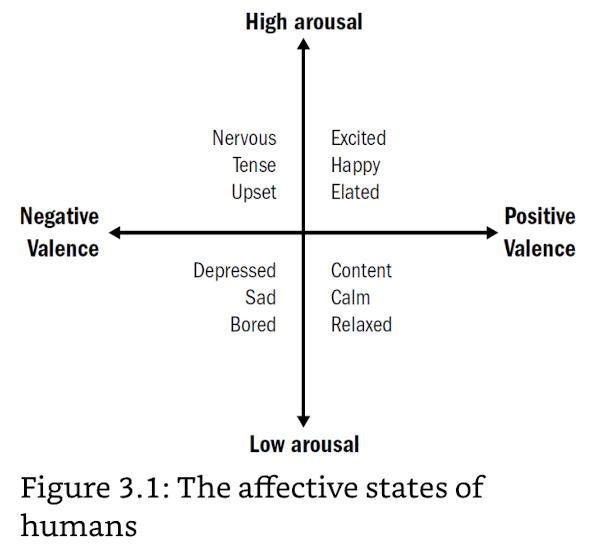
internal states modulates complex responses
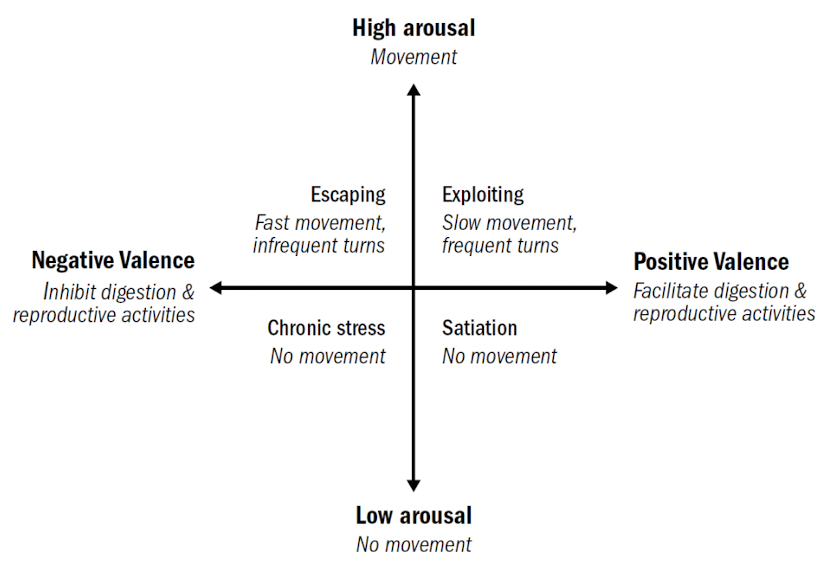
- direction (good VS bad) and entent (strong VS weak) of internal states ≈ primitive emotions
- tricks to solve sets of problems
⠀
persistence of internal state
- triggered by external stimuli
- solve the problem of hints being transient (smell of food, threat of predator)
- coral, jelly fish etc. lack affective states → emerged from steering
⠀
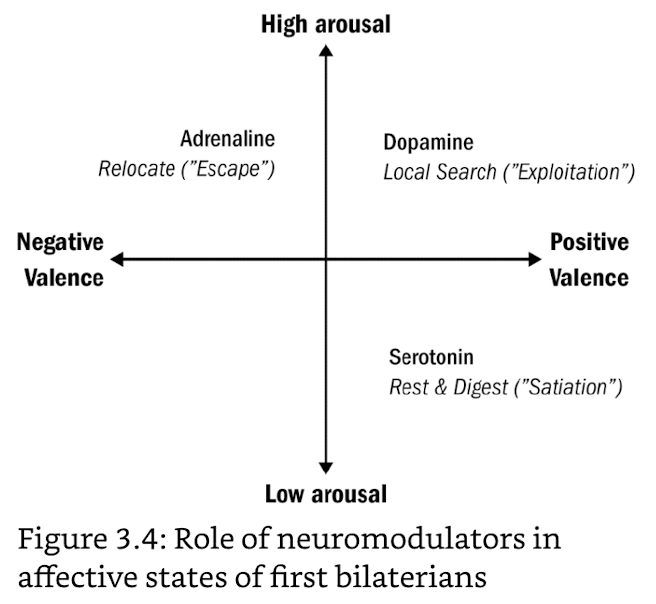
basic neurotransmitters
- dopamine
- detects food → desire (pos high arousal for exploitation)
- not signal for pleasure itself, but anticipation of future pleasure
- serotonin
- food is eaten → satiation (pos low arousal for digestion)
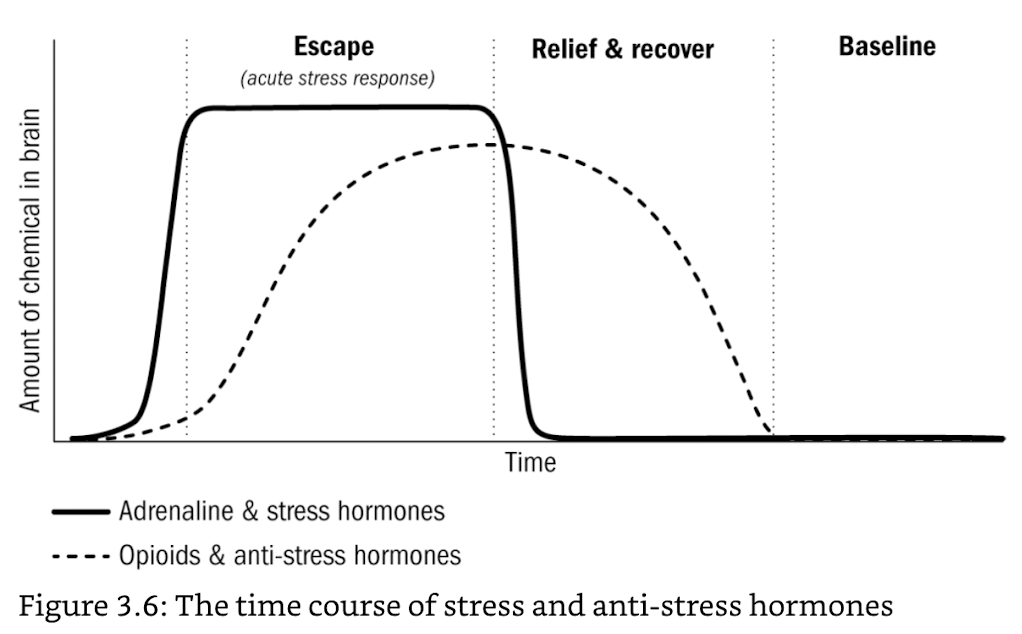
- stress hormones (e.g. adrenaline)
- detects danger → alarm (neg high arousal for flight or flight)
- acute stress response: expensive activities turned off
- opioids
- after stress response → immobile, ↑pleasure, ↓pain, no sex drive
⠀
relief state ≠ baseline
- e.g. worm starved will binge eat and pass out because: starvation → signal that food is scarce → stock up in preperation for starvation
- in general: stress → circumstances are dire → trauma response is what prepares for the next stressor
⠀
primitive depression
- acute stress: escapable neg stimuli, spend energy to do so
- chronic stress: inescapable neg stimuli, preserve energy and wait
- stress hormones + serotonin = numbness, low arousal & motivation
⠀
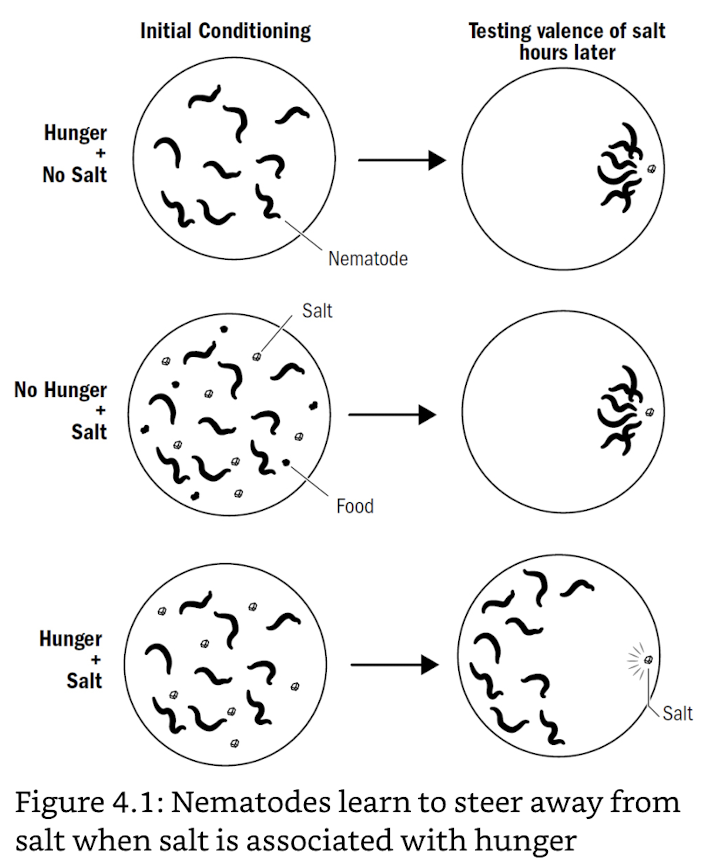
associative learning
- ability to learn associations
- between stimuli (bell & food)
- between action & consequence (lever & food)
- for variable programming on previous experience (VS invariable reflex)
- continual learning: long + short-term memory
- spontaneous recovery: broken associations reemerge after a while
- reacquisition: extinguished associations are reacquired faster than new associations (strategy against short-term changes)
- credit assignment problem: how to know which cues are meaningful
- eligibility traces: close enough to each other
- overshadowing: pick strongest cues
- latent inhibition: frequent stimuli flagged as irrelevant noise
- blocking stick to established cues and ignore others
⠀
2 Breakthrough: Reinforcement Learning
features of reinforcement learning
- complex sequence of action learned simply from trial and error
- law of effect: responses that produce good/bad effect become more/less likely to occur in that situation
- complex, indirect, over time VS associative learning: simple, direct, immediate
⠀
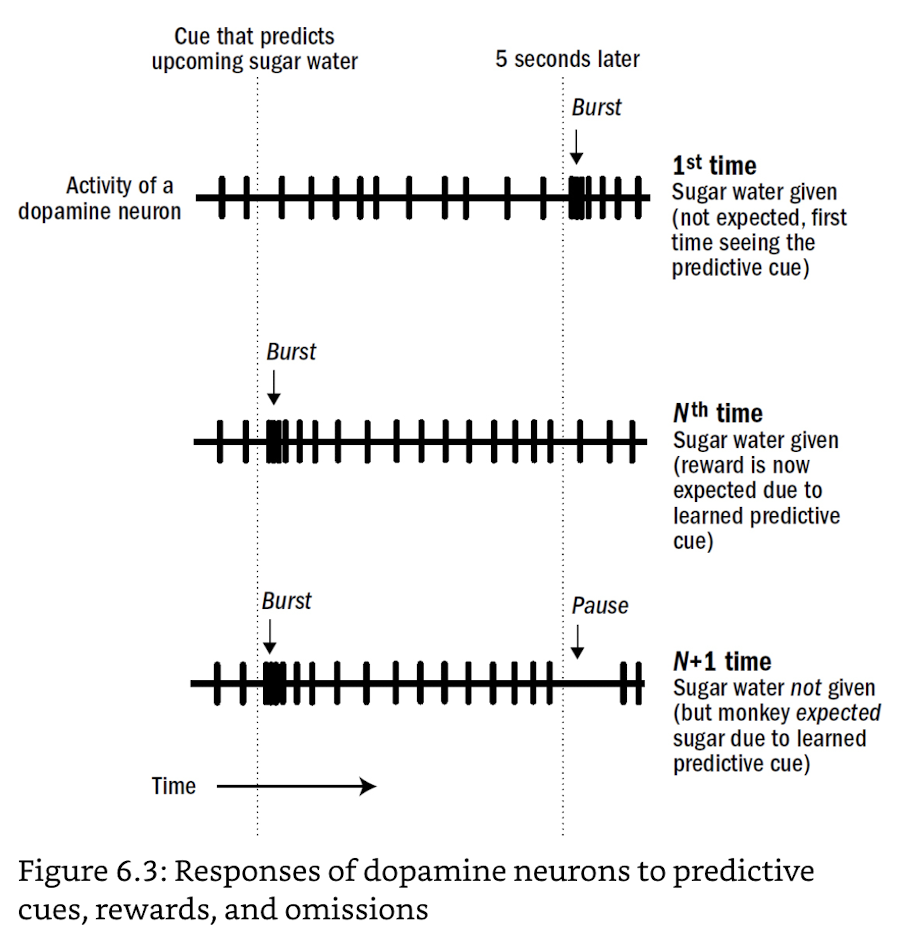
temporal credit assignment: to discern meaningful cues across time
- ↑dopamine when ↑anticipate future reward (expectation)
- ↑dopamine when ↓anticipate future penalty (relief)
- ↓dopamine when ↓anticipate future reward (disappointment)
- ↓dopamine when ↑anticipate future penalty (fear/anxiety)
- signal for reinforcement (decoupled from reward itself for it to work)
⠀
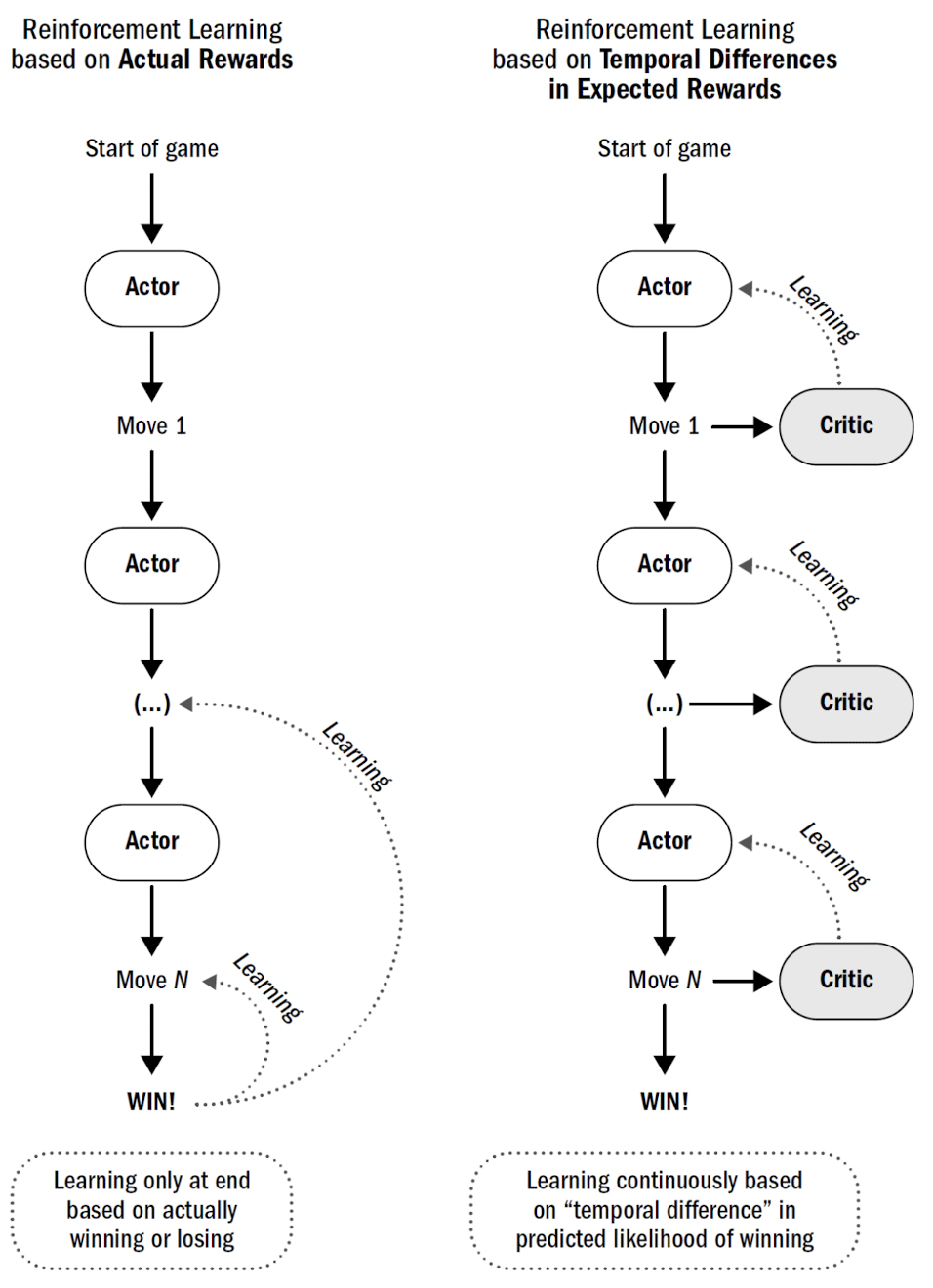
temporal difference learning in ML
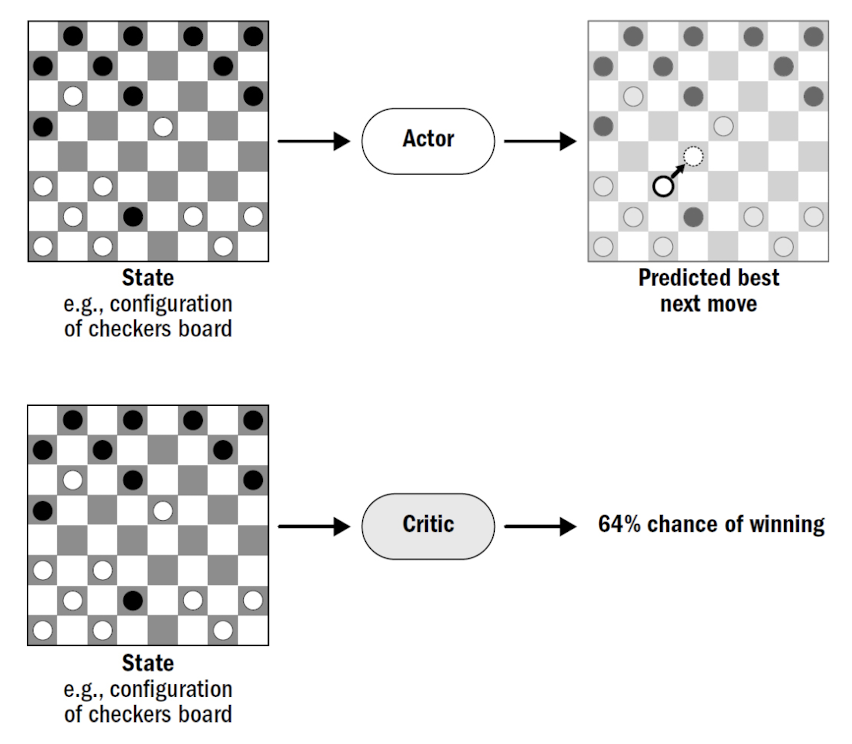
- actor: decides on action
- predictor: predict change in future reward for that action
- actor’s learning: not on actual reward/win, but the “change” predicted
⠀
temporal difference learning in vertabrates
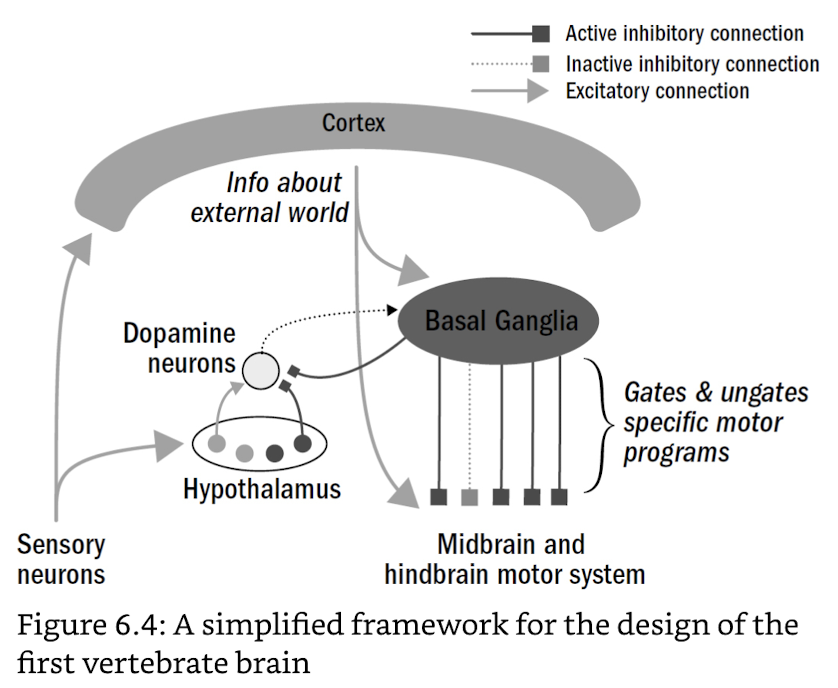
- hypothalamus: decider of actual reward
- actor: basal ganglia → motor system, learn to trigger dopamine
- critic: basal ganglia → dopamine neurons, learn to anticipate reward & judging itself on how well it predicted the value of actions before hypothalamus gives feedback on actual reward
⠀
pattern recognition
- discrimination problem (seperating similar patterns)
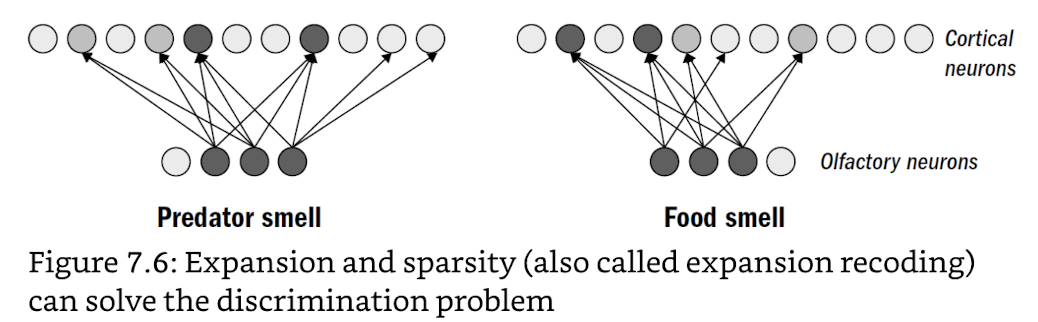
- dimensionality expansion: few inputs → many outputs
- sparsity: an input only connects to a few outputs
- generalization problem
- auto-association: neurons send synapses to nearby ones
- overwhelming/forgetting problem
- separated patterns are inherently unlikely to interfere
- learning selectively occurs with novelty and not the matched
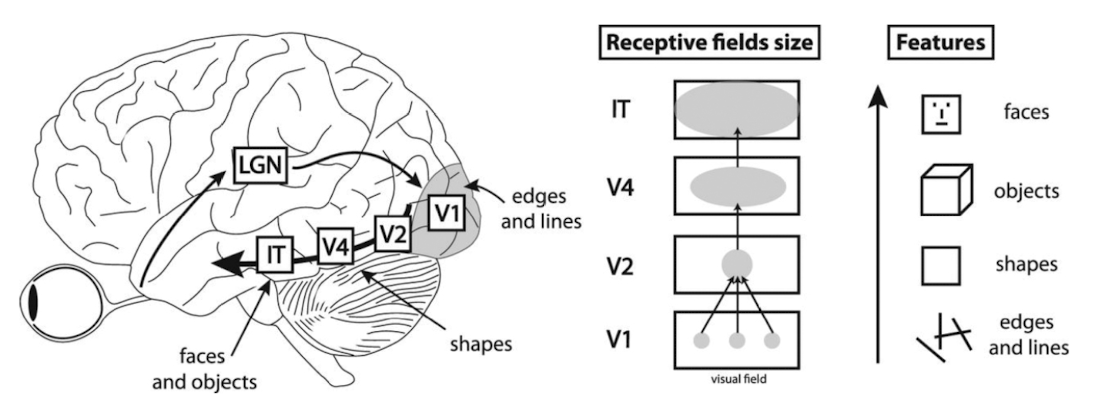
- invariance problem: different angles/pitches
- hiearchy of layers of increasing receptive field size processing increasingly wholistic and complex patterns
- each level sensitive to similar features, just in diff places
- exploitation-exploration dilemma: balancing previously reinforced and new behaviors
- reward for novelty, making exploration itself reinforcing (curiosity required for reinforcement learning to work)
- e.g. novelty triggers dopamine, though there is no external reward
⠀
internal model
- percieves its own direction in hindbrain (vestibular sense)
- percieves 3d space in hippocampus (place cells for spatial maps)
- constructs model: representation of the external world, initially for remembering locations
⠀
3 Breakthrough: Simulation
requirements for evolving simulation
- far-ranging vision
- on land much is very far → planning is better
- underwater not far → respond quickly is better
- warm-bloodedness
- evolved for nocturnal life that avoids ectothermic reptiles
- sensitive to temperature, could operate faster & stable
⠀
neocortex features
- neurons connected vertically across layers respond to similar stimuli, and their horizontal neighbors to others
- same type of neurons with identical structure for processing of different kinds of sensory information
- perception & imagination performed with same area
⠀
perception is simulation
- filling in + one at a time + cannot unperceive
- inference: we don’t perceive what is actually experienced, we pecieve a simulated reality infered from what we experience
- perception optimize for the inner simulated reality’s accuracy in predicting the external sensory input
⠀
generative: recognize by simulating
- humans optimize for how well simulated reallity predicts external sensory inputs
- Helmholtz machine
- wake phase
- recognition network observes input into hidden states, and from them generation network reconstructs into ouput
- diff between output and input backpropagated through both networks
- sleep phase
- generation from hidden state first, then recognization of the ouput into new hidden states
- diff between old and new hidden states backpropagated
- wake phase only: autoencoders; sleep phase comparable to imagining/dreaming
- unsupervised, but learns to both generalize pattern & generate novel examples of those patterns
- wake phase
⠀
above = evidence that perception is generative model creating simulation of the wolrd to match sensory inputs
4 Breakthrough: Mentalization
5 Breakthrough: Language
ML & Bio
- cleaning machine & worm nervous system
- actor/critic system & basal ganglia
- CNN & visual cortex
- Montezuma’s Revenge & curiosity mechanism
- recognize by simulation & Helmholtz machine
⠀
Other ideas
“I wrote this book because I wanted to read this book.”
Traumatic responses are protection against future dire circumstances
scrolling & gambling exploits uncertainty reinforcement
- not sure of the outcome (interesting content randomly shows up; surprising when you win at casino)
- activity itself is unrewarding, but is pursued anyway
⠀
-Max Bennett. A Brief History of Intelligence
Graphs (by Max Bennett and Rebecca Gelernter)
1
2
3